Topics covered in the article:
- Introduction: Essentials of E-Commerce marketing
- Understanding Key E-Commerce Metrics
- Popular Customer Acquisition Strategies for E-Commerce
- E-Commerce Retention Strategies to Build Long-Term Customer Relationships
- Key Stages of an E-commerce Sales Funnel
- Customer Journey Mapping for E-Commerce
- The Importance of Email and SMS Automation in E-Commerce
- Popular On-site E-Commerce Marketing Strategies
- Measuring and Optimizing E-Commerce Marketing Performance
- Conclusion
—
1. Introduction: Essentials of E-Commerce marketing
- Conversion-Focused: E-commerce aims to turn browsers into buyers fast, using tactics like urgency and optimized checkouts. Unlike SaaS with longer sales cycles, e-commerce needs quick actions.
- Product-Centric Content: Product images, reviews, and descriptions drive decisions. Unlike SaaS, e-commerce messaging is highly visual and straightforward.
- Performance Marketing & ROI Tracking: E-commerce relies on paid ads and tracks exact returns. Platforms like Google Shopping and Facebook Ads attract high-intent traffic to specific products.
- Data-Driven Testing: Constant A/B testing on ads, layouts, and pricing maximizes revenue by making quick adjustments.
- Cart Abandonment Recovery: E-commerce marketers use reminders, retargeting, and discounts to bring back customers who leave before buying.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Retaining customers is a priority, with loyalty programs, targeted emails, and personalized promotions encouraging repeat sales.
- SEO for Products: Optimized product pages drive organic traffic to specific items, not just the brand.
- Omnichannel Reach: E-commerce integrates across platforms (web, social, email, marketplaces) for consistent, accessible shopping.
- Personalization: Data on past purchases and behavior allows for tailored recommendations, unlike typical local or SaaS marketing.
- Fast, Reliable Fulfillment: Speedy, dependable delivery and easy returns are crucial, often featured in e-commerce marketing to reassure customers.
—
2. Understanding Key E-Commerce Metrics
Tracking the right metrics is crucial for effective decision-making in e-commerce. A data-driven approach to KPIs, such as conversion rate and customer acquisition cost, provides insights into where to allocate resources for maximum impact.
Key Metrics That Matter

- Conversion Rate: The percentage of visitors who make a purchase, reflecting your site’s effectiveness in turning traffic into revenue.
- Average Order Value (AOV): The average spend per transaction. Increasing AOV can directly boost profitability.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The total cost to gain a new customer, crucial for managing budgets and calculating ROI.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The total expected revenue from a customer over their relationship with your brand.
- Retention Rate: The percentage of returning customers, reflecting customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Cart Abandonment Rate: Measures the frequency at which customers leave items in their cart, helping identify obstacles to conversion.
—
3. Popular Customer Acquisition Strategies for E-Commerce
In the competitive world of e-commerce, customer acquisition is crucial for long-term growth and profitability. The process of attracting new customers involves more than just getting them to visit your site; it’s about building a sustainable strategy that engages visitors, converts them, and, ideally, retains them for future purchases. In this article, we’ll explore key customer acquisition strategies with examples from diverse e-commerce industries.

—
3.1. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
SEO is the foundation of any solid e-commerce acquisition strategy, focusing on improving your store’s visibility on search engines. When customers search for a product, they often turn to Google. Appearing on the first page of results for relevant keywords can drive organic traffic to your site.
Example: Consider a skincare brand like Glossier. Their SEO strategy focuses on long-tail keywords like “hydrating skincare for dry skin.” By creating blog content, product pages, and FAQ sections around these keywords, they attract visitors searching for specific skincare solutions, improving their chances of conversion.
Tips for SEO Success:
– Conduct keyword research to target both broad and niche keywords.
– Optimize product descriptions and blog posts with relevant keywords.
– Ensure your site is mobile-friendly and has a fast load speed.
– Build backlinks by partnering with bloggers and other websites.
—
3.2. Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising
PPC campaigns, like Google Ads or social media ads, allow e-commerce brands to drive targeted traffic to their site. PPC is especially effective for product-specific searches or targeting users based on demographics, interests, or behaviors.
Example: A fitness apparel brand, like Gymshark, might run a Google Ads campaign targeting keywords like “best workout leggings.” On social media, they might target young adults interested in fitness and wellness. This highly focused approach helps Gymshark attract potential buyers already interested in fitness gear.
Tips for PPC Success:
– Set a clear budget and track ROI to manage costs.
– Use A/B testing for ad creatives and keywords.
– Focus on retargeting ads for visitors who have shown interest in your products but didn’t convert.
—
3.3. Social Media Marketing
Social media marketing is a powerful way to attract new customers by creating engaging content and building brand presence. Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok offer both organic and paid opportunities to reach new audiences.
Example: ColourPop Cosmetics, a beauty brand, uses Instagram and TikTok to showcase vibrant visuals and tutorials. They encourage user-generated content by reposting customer reviews, unboxing videos, and makeup looks, creating a community around their brand and reaching new potential customers.
Tips for Social Media Success:
– Post regularly and engage with your audience.
– Use a mix of content: tutorials, product demos, customer testimonials, etc.
– Run targeted social media ads, especially on platforms where your audience is most active.
—
3.4. Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing involves partnering with influencers who align with your brand values and audience. By leveraging influencers’ established relationships with their followers, you can reach new customers who trust these voices.
Example: Fashion Nova frequently collaborates with influencers in the fashion and lifestyle space, especially on Instagram. By doing so, they tap into these influencers’ follower bases and position their products as trend-worthy and aspirational, driving awareness and conversions.
Tips for Influencer Marketing Success:
– Choose influencers whose audience aligns with your brand.
– Set clear campaign goals, such as brand awareness or direct sales.
– Use discount codes or affiliate links to track conversions.
—
3.5. Email Marketing
Email marketing remains one of the most effective channels for customer acquisition. By collecting email addresses, you can nurture leads and keep potential customers engaged with your brand. Building an email list also helps you retarget visitors who may not have converted initially.
Example: HelloFresh, a meal kit delivery service, captures email addresses from visitors interested in recipes and meal-planning content. They send new subscribers a welcome series that offers discounts on their first order, which helps to convert them into paying customers.
Tips for Email Marketing Success:
– Offer incentives like discounts or exclusive content for sign-ups.
– Segment your email list based on behaviors and preferences.
– Use personalization to improve open rates and engagement.
—
3.6. Content Marketing
Content marketing focuses on creating valuable content to attract and engage potential customers. By offering informative and entertaining content, you build credibility and keep your brand top-of-mind for consumers who may eventually convert into paying customers.
Example: An outdoor gear brand like REI creates blog posts and videos about outdoor adventure tips, gear recommendations, and destination guides. This content attracts outdoor enthusiasts to their site, building a relationship that can lead to future purchases.
Tips for Content Marketing Success:
– Create a blog or resource center with articles relevant to your niche.
– Use a mix of written, video, and visual content.
– Optimize content for SEO to attract organic traffic.
—
3.7. Referral Programs
Referral programs encourage existing customers to refer new ones, often by offering rewards like discounts or cash incentives for successful referrals. This strategy leverages word-of-mouth marketing, which is one of the most trusted sources of information for consumers.
Example: Dropbox successfully used a referral program by offering both the referrer and the referred user additional storage space. This strategy helped them gain new customers while rewarding loyal users.
Tips for Referral Program Success:
– Offer valuable incentives for both referrers and referees.
– Make the referral process simple and easy to share.
– Track referrals to measure the program’s effectiveness.
—
3.8. Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing allows you to partner with bloggers, websites, or influencers who promote your products to their audiences. Affiliates earn a commission on sales generated from their referrals, which incentivizes them to promote your brand.
Example: Amazon has a robust affiliate program that allows website owners, bloggers, and influencers to earn a percentage on products sold through their unique affiliate links. This enables Amazon to reach a vast audience across many niche sites without upfront costs.
Tips for Affiliate Marketing Success:
– Choose affiliates whose audience aligns with your target market.
– Offer competitive commissions to attract high-quality affiliates.
– Provide affiliates with creative assets, such as banners or product images.
—
Customer acquisition is a multi-faceted process, especially in e-commerce, where competition is fierce. By implementing a mix of these strategies, you can effectively reach and convert new customers. The key is to continuously test, refine, and adapt your approach based on customer data and market trends. With the right strategies, any e-commerce business can grow its customer base and build a loyal audience.
3.9. Retargeting
Retargeting focuses on re-engaging visitors who have shown interest in your products but left without purchasing. Retargeting ads are typically displayed on social media or across the Google Display Network, keeping your products visible to potential customers as they browse other sites.
Example: A furniture brand like Wayfair might retarget visitors who viewed a specific item, showing them the same or similar products across the web. This gentle reminder often leads users back to the site to complete the purchase.
Tips for Retargeting Success:
– Use dynamic ads that show customers products they viewed or added to their cart.
– Set frequency caps to avoid overwhelming users with too many ads.
– Consider using retargeting email campaigns for abandoned carts.
—
4. E-Commerce Retention Strategies to Build Long-Term Customer Relationships
In e-commerce, success relies not only on acquiring new customers but also on retaining them. By focusing on retention strategies, brands can increase customer lifetime value (LTV), encourage repeat purchases, and build loyal relationships that drive long-term growth. Here, I’ll explore essential e-commerce retention strategies with examples from various industries, all designed to deepen customer connections and drive repeat sales.

4.1 Personalized Customer Experiences
Personalized experiences can make customers feel valued and create a sense of connection with your brand. By tailoring recommendations, emails, and content based on individual preferences and past behaviors, brands can boost engagement and loyalty.
Example: Amazon uses personalized recommendations based on customer browsing and purchase history. For instance, a customer who buys fitness equipment may later see workout apparel suggestions, making the experience feel tailored and relevant.
Tips for Personalization:
- Use customer data to deliver customized product suggestions.
- Personalize email content and subject lines based on customer history.
- Incorporate personalized elements into loyalty program interactions.
4.1 Loyalty and Rewards Programs
Loyalty programs incentivize repeat purchases by rewarding customers for their continued support. Offering points, discounts, or exclusive rewards can make customers feel valued, encouraging them to return and increasing their lifetime value.
Example: Sephora’s Beauty Insider program offers points for every purchase, redeemable for products, birthday gifts, and exclusive access to new products. This rewards system keeps customers coming back and creates a sense of exclusivity.
Tips for Effective Loyalty Programs:
- Keep the program straightforward to understand and join.
- Offer meaningful rewards that add value for members, like discounts or perks.
- Use tiered levels to encourage higher spending and reward top customers.
4.3 Regular, Value-Driven Email Marketing
Email marketing remains one of the most powerful retention tools when used to provide ongoing value. By sending content like tips, recommendations, exclusive offers, and updates, brands can stay top-of-mind with customers and encourage repeat business.
Example: HelloFresh sends tailored recipe suggestions, cooking tips, and meal ideas based on each customer’s past orders. These emails reinforce HelloFresh’s value by showcasing convenience and variety, encouraging customers to stay subscribed.
Tips for Successful Email Campaigns:
- Segment your email list by customer preferences, behavior, and purchase history.
- Personalize messages with reorder reminders or special offers.
- Balance promotional content with helpful information to avoid overwhelming recipients with sales emails.
4.4 Customer Feedback and Continuous Improvement
Collecting and acting on customer feedback demonstrates that your brand values their experience. By listening to customer input and responding with relevant changes, you can enhance satisfaction and build trust, leading to greater retention.
Example: Glossier uses customer feedback from social media and surveys to inform new product development. This feedback loop helps Glossier deliver products that resonate with customers, fostering loyalty and community.
Tips for Creating Feedback Loops:
- Use post-purchase surveys to gather insights on customer satisfaction.
- Monitor social media and reviews to identify recurring issues or improvement opportunities.
- Address negative feedback promptly and communicate updates or changes based on customer suggestions.
4.5 Subscription Models
Subscription models provide ongoing value while creating a consistent revenue stream. By offering a subscription option, e-commerce brands can encourage customers to stick around, fostering a long-term relationship.
Example: Dollar Shave Club delivers grooming products on a regular schedule, offering convenience and removing the need to reorder. Subscribers stay engaged with the brand while enjoying an effortless experience.
Tips for Subscription Success:
- Offer flexible plans that accommodate different customer needs.
- Provide exclusive perks for subscribers, like discounts or early access.
- Send reminder emails before renewals to allow customers to adjust their plans as needed.
4.6 Exclusive Offers for Returning Customers
Exclusive offers for returning customers are a simple but effective way to encourage repeat purchases. These offers show customers they’re valued, giving them a reason to return to your store over competitors.
Example: ASOS, a popular fashion retailer, provides returning customers with personalized discounts, especially after a period of inactivity. These offers rekindle interest in the brand and help drive repeat sales.
Tips for Creating Exclusive Offers:
- Use customer data to tailor offers based on shopping history.
- Send “We Miss You” emails with personalized discounts to re-engage lapsed customers.
- Reward loyalty program members with early access to sales or new products.
4.7 Retargeting Campaigns
Retargeting is not just for new visitors; it’s also a powerful way to bring back existing customers who haven’t purchased recently. Retargeting campaigns keep your brand visible across the web, encouraging customers to return to complete a purchase.
Example: Wayfair uses retargeting ads to showcase items previously viewed by customers, such as furniture or decor. By keeping the product in front of the customer, Wayfair encourages them to complete their purchase.
Tips for Retargeting Success:
- Use dynamic ads that feature items customers previously viewed or added to their cart.
- Set frequency caps to avoid overwhelming customers with ads.
- Consider abandoned cart emails to offer a small incentive and encourage completion.
4.8 Exceptional Customer Service
Customer service is a crucial factor in retention, as customers often remember their experiences with a brand’s support team. By providing quick, friendly, and helpful customer support, brands show they care, which builds loyalty.
Example: Zappos is known for its exceptional customer service, with representatives empowered to go above and beyond to solve customer issues. This approach has earned Zappos a loyal following and a reputation for outstanding support.
Tips for Superior Customer Service:
- Train support teams to prioritize empathy and customer needs.
- Offer multiple support options, like live chat, email, and phone.
- Follow up with customers after issue resolution to reinforce satisfaction.
4.9 Community Building and Social Engagement
Community building can turn customers into loyal advocates by creating a sense of belonging. Social media, blogs, and online forums allow customers to connect with your brand and other customers, reinforcing their loyalty.
Example: Patagonia fosters a strong community of environmentally conscious customers through its social media, blog, and “Worn Wear” initiative, which promotes recycling and repairing products. This values-driven approach strengthens customers’ emotional connection to the brand.
Tips for Building a Community:
- Create online groups or social media pages where customers can engage.
- Share user-generated content, like photos and testimonials, to boost community involvement.
- Reinforce values that resonate with your audience to build a deeper connection.
4.10 Consistent Product Quality and Improvement
Maintaining product quality is essential to retaining customers. When customers trust the quality of your products, they’re more likely to return. Additionally, ongoing product improvements keep customers interested and engaged.
Example: Apple maintains customer loyalty by consistently delivering high-quality products and enhancing them over time. Each new product release often incorporates user feedback, demonstrating Apple’s commitment to quality and customer needs.
Tips for Maintaining Quality and Improvement:
- Ensure all products meet high standards of quality and reliability.
- Collect customer feedback to inform product upgrades and new features.
- Regularly introduce improvements or updates based on evolving customer needs.
Customer retention is the foundation of a thriving e-commerce business. By focusing on strategies like personalization, loyalty programs, excellent service, and community building, brands can create long-lasting relationships that encourage repeat business and brand advocacy. When customers feel valued, engaged, and appreciated, they’re more likely to stick around, making retention strategies a critical investment for sustainable growth.
5. Key Stages of an E-commerce Sales Funnel
An e-commerce funnel maps the journey from potential customer to loyal buyer. While the exact steps can vary, successful funnels generally include five main stages:
- Awareness (Top of Funnel – TOFU)
At the funnel’s top, the goal is to create brand awareness. Here, you engage with potential customers about their pain points and educate them on possible solutions through content marketing, SEO, or ads. Effective keyword research helps align your message with what your target audience is searching for, allowing you to reach them at a low cost. - Consideration/Evaluation (Middle of Funnel)
In the middle stage, prospects are aware of their problem and ready to explore solutions. Your role here is to present your brand as the best choice, positioning it as the ideal solution. The focus is on converting visitors into leads, often through email subscriptions or special offers that keep them engaged. - Purchase (Bottom of Funnel)
Here, the customer decides to buy. Every previous interaction has built trust, guiding them toward this moment. This stage is where they commit, completing their journey from prospect to customer. - Post-Purchase
After the sale, your engagement continues. Following up with customers via email or targeted offers encourages them to make further purchases. You might also cross-sell or upsell related products, deepening the relationship. - Repeat Purchase
The ultimate goal is repeat business. Retaining customers is more cost-effective than acquiring new ones, and loyal buyers drive profit and brand advocacy. This stage aims to build lifetime value through continued engagement, testimonials, and recommendations.

Flexibility in the Funnel
The sales funnel should be adaptable. Not every customer takes the same path, and the journey may be shorter or longer depending on individual needs. A successful funnel mirrors the buyer’s journey, adjusting to different customer profiles and engagement levels.
—
6. Customer Journey Mapping for E-Commerce
Alternative approach to analizing customer journey are Customer Journey Maps.
6.1. The difference between Sales Funnel and Customer Journey Map
The E-commerce Sales Funnel focuses on guiding potential customers through specific stages that lead to a purchase—moving them from awareness to consideration, and ultimately, to buying and repeat purchases. It’s a business-centered tool designed to maximize conversions at each stage.
In contrast, the E-commerce Customer Journey Map is a customer-centered view that illustrates the complete experience customers have with a brand, from initial discovery through post-purchase interactions.
This map captures customers’ emotions, needs, and pain points at each touchpoint, providing insights into how they perceive and interact with the brand.
In short:
- Sales Funnel: Business-oriented, focused on driving conversions at each funnel stage.
- Customer Journey Map: Customer-oriented, detailing the emotional and experiential path from discovery to loyalty.
6.1. Elements and Example of a Customer Journey Map
An e-commerce customer journey map typically includes these main elements:
- Stages of the Journey: Key phases customers go through, such as Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, and Post-Purchase. Each stage reflects a different mindset and level of interaction with the brand.
- Customer Goals and Needs: What customers aim to achieve at each stage—like finding information, comparing products, or seeking support after purchase. This element helps in understanding motivations.
- Touchpoints: Specific points of interaction between the customer and the brand across channels, such as website visits, email, social media, customer service, or in-app messaging.
- Customer Emotions and Pain Points: How customers feel and what challenges or frustrations they encounter at each stage. Identifying emotional responses helps brands improve experiences and address potential drop-off points.
- Actions: What the customer actively does at each stage, such as searching for products, reading reviews, or completing a purchase. This shows the behavior patterns associated with each stage.
- Opportunities for Improvement: Insights on how to optimize the experience at each stage. This could mean simplifying checkout, enhancing product info, or offering better post-purchase support.
Each of these elements helps brands design more engaging, empathetic experiences that meet customer needs and expectations at every stage of the journey.
Some examples:



6.2 Steps to Map the Customer Journey
- Identify Customer Segments: Segmenting customers reveals diverse needs and behaviors.
- Mapping Touchpoints: Define each interaction from awareness to purchase.
- Evaluating Conversion Drivers and Barriers: Identifying and addressing friction points improves the overall journey.
6.3 Should you design both, the Sales Funnel, and the Customer Journey Maps?
Yes, an e-commerce store should design both a Sales Funnel and Customer Journey Maps because they serve complementary purposes and together provide a complete view of the customer experience.
- Sales Funnel: This tool is business-focused, aiming to optimize conversion rates at each stage (awareness, consideration, purchase, post-purchase). By understanding and refining each funnel stage, stores can guide more potential customers toward making purchases and returning as loyal buyers.
- Customer Journey Map: This is customer-centered, detailing the entire experience from the customer’s perspective, including emotions, needs, and challenges across various touchpoints. Mapping the journey helps identify areas where the experience can be improved, like addressing pain points in customer service, enhancing the checkout process, or improving product information.
Together, the Sales Funnel helps drive conversions, while the Customer Journey Map improves the quality of each customer interaction. When both are in place, the store can boost both customer satisfaction and conversion rates, creating a smoother path to loyalty and higher lifetime value.
—
7. The Importance of Email and SMS Automation in E-Commerce
Email and SMS automation are essential in e-commerce as they streamline customer communication, boost engagement, and increase sales. By automatically sending tailored messages at key moments, businesses can nurture leads, encourage repeat purchases, and build lasting customer relationships—all with minimal manual effort.
7.1. Why Email and SMS Automation Matter
- Increases Conversions: Automated messages reach customers at critical moments in their journey, such as when they abandon a cart or browse specific products. These timely nudges can remind customers to complete purchases, driving up conversion rates.
- Enhances Customer Retention: Post-purchase follow-ups, such as thank-you messages or product recommendations, help to keep customers engaged and encourage repeat business. Automation also allows for consistent, valuable communication that builds loyalty over time.
- Improves Customer Experience: Personalization is easier with automation. Sending relevant, timely messages based on customers’ behavior (like birthday discounts or order updates) enhances the shopping experience and makes customers feel valued.
- Saves Time and Resources: Automation frees up time for your team by handling repetitive communication tasks. This means your team can focus on other priorities, while the automated system continuously supports customer engagement and sales.
7.2. Examples of Effective E-commerce Automations
- Welcome Series
Triggered when someone subscribes to the newsletter or creates an account, this series introduces the brand, offers a discount, and highlights popular products. For instance, a welcome email could say, “Thanks for joining! Here’s 10% off your first order!” - Abandoned Cart Reminders
These automated reminders help recover potential lost sales. If a customer leaves items in their cart, a reminder can be sent via email or SMS with a friendly nudge like, “Still thinking about this? Here’s a 10% discount to complete your purchase.” - Product Recommendations and Cross-Selling
After a purchase, follow-up emails or texts can suggest related items or complementary products. For example, if a customer buys running shoes, an automated message could suggest fitness gear or socks. - Order and Shipping Updates
Keep customers informed about their purchase progress with automated updates, such as order confirmation, shipping notifications, and delivery updates. This helps build trust and reduce customer inquiries. - Replenishment Reminders
For products with a recurring need (like skincare or supplements), reminders can be set based on estimated usage times. A message might say, “Time to restock on your skincare essentials—click here to reorder!” - Post-Purchase Follow-Up
After a purchase, an email or SMS can check in with the customer, offer tips on product usage, or invite them to leave a review. This builds engagement and encourages feedback that can help improve the product or service. - Win-Back Campaigns
If a customer hasn’t purchased in a while, a win-back email or SMS can reignite their interest, often with a special offer or reminder of why they loved the brand initially.



Email and SMS automation help e-commerce stores deliver timely, personalized messages at scale, driving sales, improving customer satisfaction, and building loyalty. By implementing automations like welcome series, abandoned cart reminders, and replenishment notices, brands can create a seamless, supportive customer experience that encourages long-term engagement and growth.
—
8. Popular On-site E-Commerce Marketing Strategies
On-site e-commerce marketing strategies focus on optimizing the user experience on the website itself, helping to guide visitors from discovery to purchase smoothly.
Some key on-site strategies are:
- Personalized Product Recommendations
- Showing customers products they might like based on their browsing or purchase history helps keep them engaged and can increase average order value.
- Pop-Ups and Exit-Intent Offers
- Strategically timed pop-ups, such as welcome offers or exit-intent discounts, can capture emails or offer discounts to prevent users from leaving.
- Cart Abandonment Messages
- Displaying a reminder or offering an incentive if a user has items in their cart but hasn’t checked out. Some sites also have pop-ups for items left in the cart if the user navigates away.
- Live Chat and Chatbots
- Live chat and AI-powered chatbots provide immediate support and can answer common questions about products, shipping, and returns, helping prevent customer drop-off.
- Customer Reviews and Ratings
- Displaying product reviews and ratings builds trust and provides social proof, which is crucial for new customers considering a purchase.
- Limited-Time Promotions and Urgency Tactics
- Countdown timers, “low stock” alerts, and limited-time offers create urgency, encouraging users to act quickly and avoid missing out.
- Wishlist and Save-for-Later Options
- Allowing users to save items in a wishlist or “save for later” section can encourage return visits and reduce the need for repeated browsing.
- Product Bundling and Cross-Selling
- Grouping related products together (product bundling) or suggesting complementary products (cross-selling) can increase the average order value.
- Dynamic Search and Filter Options
- Improving the search bar with predictive text, filters, and sorting options helps customers find exactly what they’re looking for quickly.
- Clear Shipping Information and Offers
- Displaying shipping costs, estimated delivery times, and any free shipping offers clearly on product pages and in the cart helps prevent checkout abandonment.
- Social Proof Integrations
- Showing real-time data, like recent purchases or “trending items,” helps create a sense of activity and popularity around certain products.
- Loyalty Program Reminders
- If the store has a loyalty program, placing reminders about points or rewards available on the product or checkout pages can incentivize repeat purchases.
- Enhanced Product Visuals and Videos
- High-quality images, zoom features, 360-degree views, and videos help customers better visualize products, leading to more confident purchasing decisions.
Read a full article about on-site marketing for e-commere with examples from the best brands here.
Few on-site campaign examples:
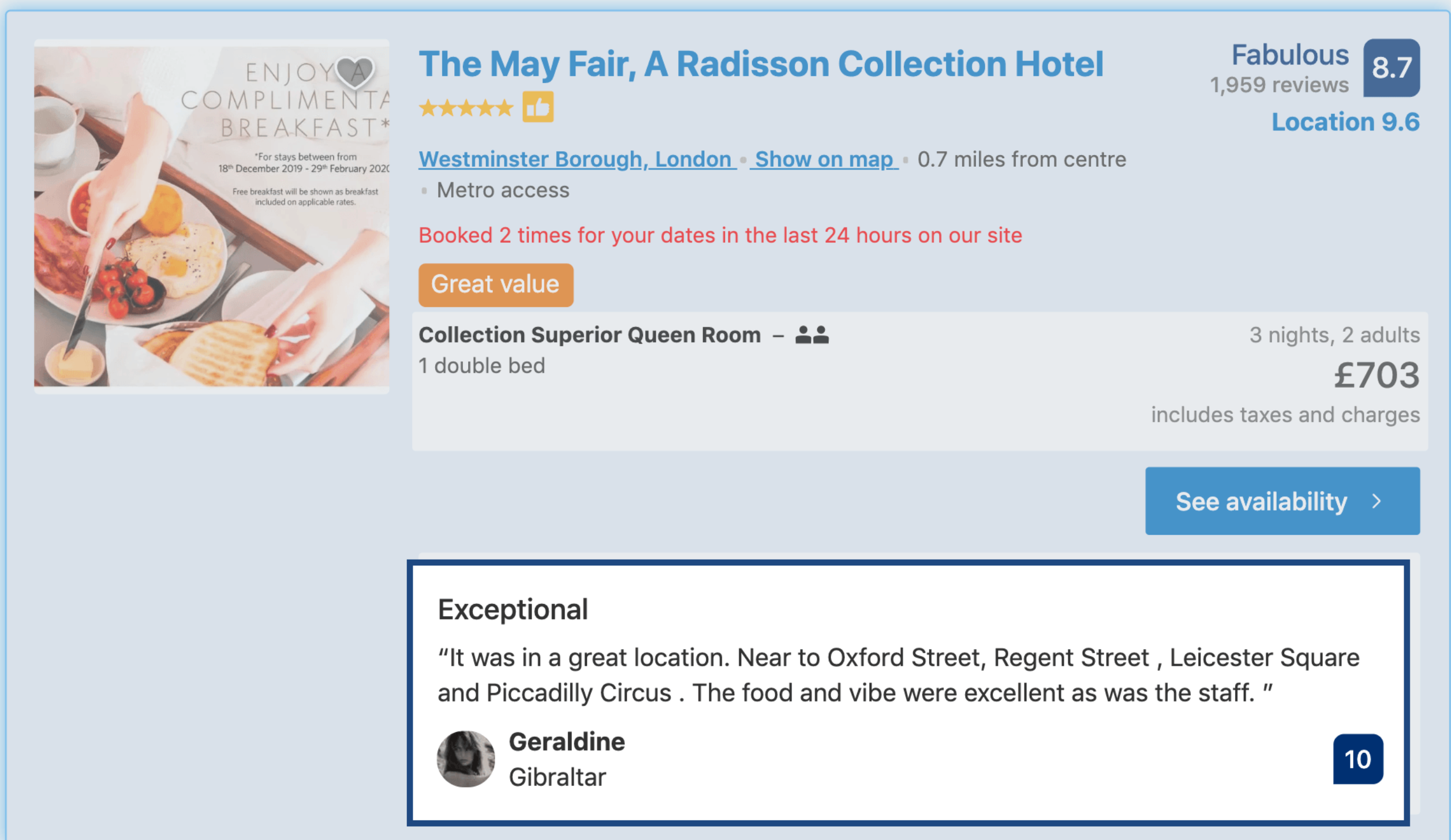
Social proof example
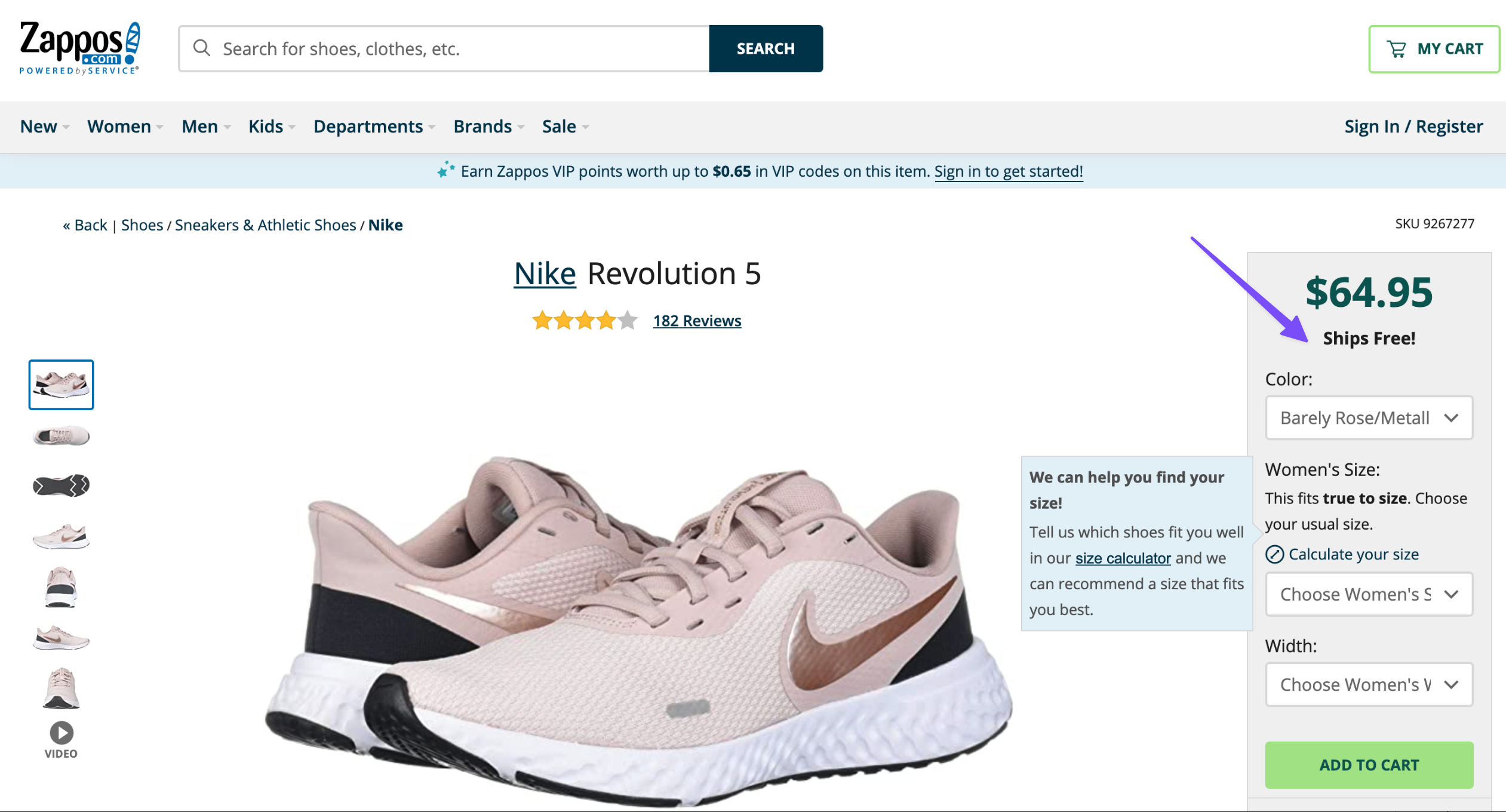
Clear shipping information
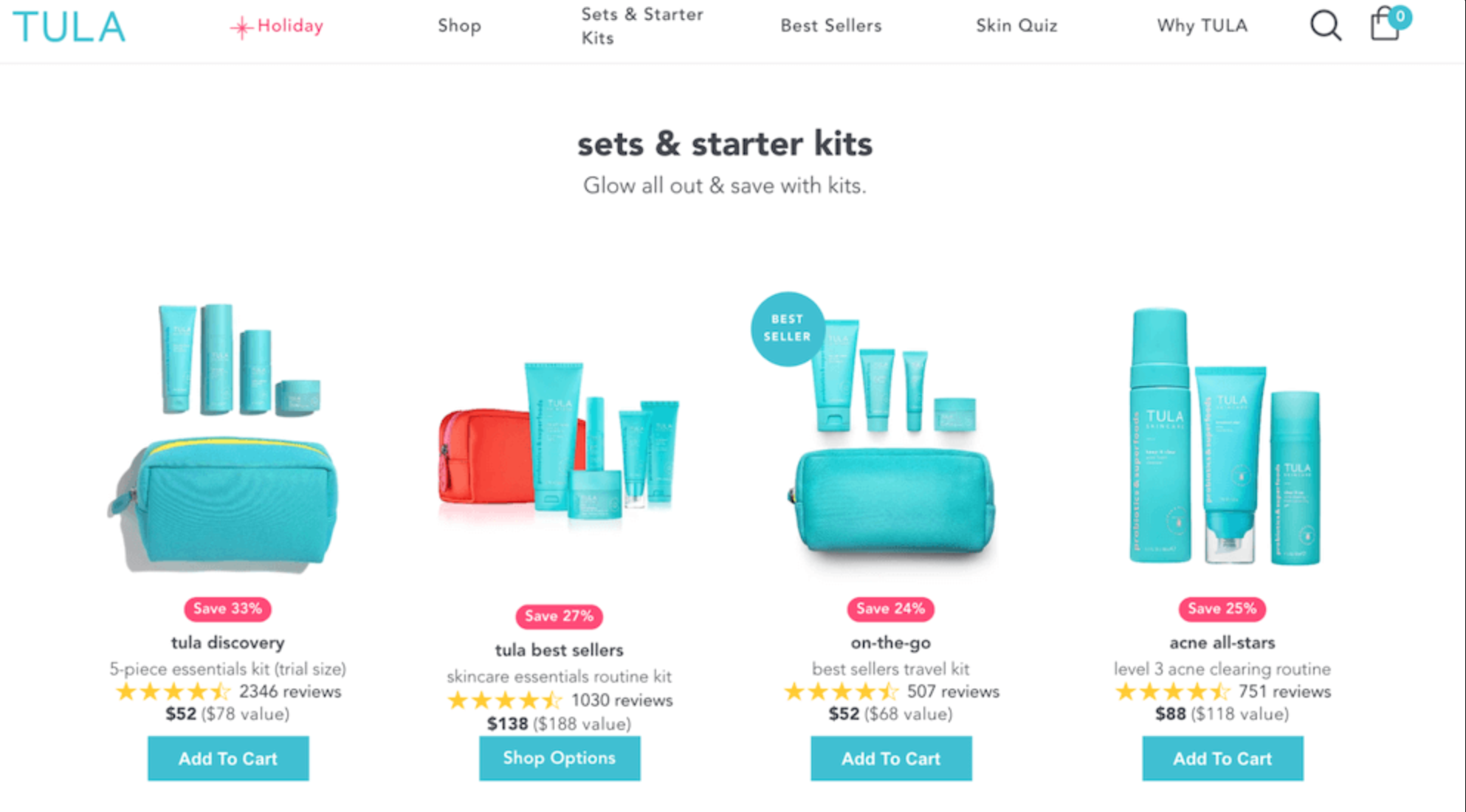
Strategic bundling example
9. Measuring and Optimizing E-Commerce Marketing Performance
9.1 Analyzing Key Metrics and Adjusting Strategies
Regular analysis of KPIs like conversion rate, CAC, and CLV allows for adjustments that improve efficiency and growth.
9.2 A/B Testing for Continuous Improvement
Experimenting with website elements, email copy, and ad creatives reveals what resonates most with customers, driving better results.
—
10. Conclusion: Building a Profitable E-Commerce Business Through Data-Driven Marketing
To build a thriving e-commerce business, balancing creativity with data is essential. By optimizing each stage of the customer journey and regularly analyzing metrics, e-commerce businesses can create strategies that drive growth and sustainability. Embracing a comprehensive, data-backed approach can turn an online store into a profitable, scalable enterprise.



